Qualitative nursing research is a powerful tool for understanding the lived experiences and perspectives of patients, nurses, and other healthcare stakeholders. By delving into the complexities of human experiences, qualitative research illuminates the nuances of care, identifies areas for improvement, and ultimately, contributes to the betterment of nursing practice. However, crafting a high-quality qualitative nursing research paper requires more than just collecting data; it demands a rigorous and systematic approach to ensure the validity and impact of your findings.
This comprehensive guide provides a step-by-step framework for navigating the intricacies of writing a qualitative nursing research paper. From conceptualizing your study to disseminating your results, we explore key aspects of the process, emphasizing the unique challenges and opportunities presented by qualitative research.
What is a Qualitative Research Paper?
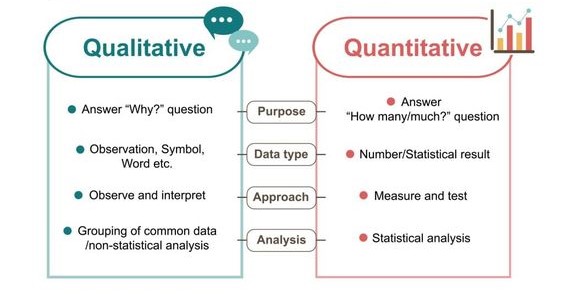
A qualitative research paper is a scholarly work that explores and analyzes non-numerical data to gain in-depth understanding of a particular phenomenon, experience, or perspective. Unlike quantitative research, which focuses on measuring and quantifying data, qualitative research delves into the "why" and "how" behind human experiences and social interactions.
Here are some key characteristics of a qualitative research paper:
- Focuses on Meaning and Understanding: Qualitative research aims to uncover the subjective experiences, beliefs, values, and motivations of individuals or groups. It seeks to understand the meaning people attribute to their experiences and how they interpret the world around them.
- Uses Non-Numerical Data: Qualitative research relies on data that cannot be easily measured or quantified, such as words, images, symbols, and observations. Examples of data sources include:
- Interviews: In-depth conversations with participants to explore their perspectives and experiences.
- Focus Groups: Facilitated discussions among a group of participants to explore shared experiences and perspectives.
- Observations: Observing participants in their natural settings to document their behaviors and interactions.
- Document Analysis: Studying existing documents, such as medical records, patient journals, and organizational reports, to gain insights into the phenomenon of interest.
- Employs Inductive Reasoning: Qualitative research typically employs an inductive approach, starting with specific observations and then developing broader themes and interpretations from the data. Researchers often use iterative analysis techniques to refine their understanding as they explore the data.
- Focuses on Context: Qualitative research recognizes that human experiences are shaped by their context, including social, cultural, and historical factors. Researchers strive to understand how these factors influence the experiences of their participants.
- Relies on Rigorous Methodology: Despite its focus on non-numerical data, qualitative research follows a rigorous methodology to ensure the validity and reliability of its findings. This includes:
- Clearly defined research question: The research question must be specific, focused, and grounded in a relevant area of study.
- Appropriate qualitative approach: The chosen qualitative approach (e.g., phenomenology, grounded theory, ethnography) should align with the research question and the type of data being collected.
- Systematic data analysis: The data analysis process should be systematic and transparent, using established qualitative methods to identify themes, patterns, and relationships within the data.
- Ethical considerations: Qualitative researchers must adhere to ethical principles, including informed consent, confidentiality, and participant well-being.
- Presents Findings in a Narrative Format: Qualitative research papers typically present findings in a narrative format, using rich descriptions, direct quotes from participants, and examples to illustrate key themes and insights.
Examples of Qualitative Nursing Research Topics:
- Exploring the lived experiences of patients with chronic pain.
- Understanding the challenges and rewards of nursing care in a particular setting.
- Analyzing the communication patterns between nurses and patients.
- Investigating the impact of cultural differences on nursing practice.
Qualitative research is an essential tool for understanding the complexities of human experiences and informing best practices in nursing and other healthcare fields. It provides valuable insights into the social, cultural, and emotional dimensions of care, leading to a deeper understanding of patients' needs and the challenges faced by healthcare professionals.
Steps for Writing a Qualitative Nursing Research Paper
1. Define Your Research Question and Conceptual Framework
Before embarking on data collection, it is crucial to establish a clear and focused research question that drives your entire study. This question should be grounded in a specific area of nursing practice, reflecting the existing knowledge gap you aim to address.
Example:
- Research Question: How do nurses experience emotional exhaustion when caring for patients with chronic pain?
Once your research question is defined, consider the theoretical framework that will guide your investigation. Choose a framework that aligns with your research question and provides a lens through which to interpret your data.
Example:
- Conceptual Framework: The Theory of Caring by Jean Watson, which emphasizes the importance of human connection and compassion in nursing practice.
2. Choose a Suitable Qualitative Approach
The choice of qualitative research approach is central to the validity and rigor of your qualitative nursing research paper. Different approaches offer unique methodologies and perspectives, each suited for specific research goals.

Common Qualitative Approaches:
- Phenomenology: Exploring the lived experiences of individuals and understanding the meaning they attribute to their experiences.
- Grounded Theory: Developing a theory from data, uncovering patterns and relationships within the data itself.
- Ethnography: Studying a particular cultural group or setting, observing and interpreting the shared practices, beliefs, and values.
- Case Study: In-depth exploration of a specific individual, group, or event, examining multiple sources of data.
Selecting the appropriate approach depends on your research question and the nature of the phenomenon you aim to investigate.
Example:
- To understand the lived experiences of nurses caring for patients with chronic pain, a phenomenological approach might be most suitable.
3. Recruit Participants and Gather Data
Participant recruitment is a critical aspect of qualitative nursing research. It is essential to select participants who can provide rich and insightful data relevant to your research question.
Strategies for Participant Recruitment:
- Purposeful Sampling: Intentionally selecting participants based on specific criteria relevant to your research question.
- Snowball Sampling: Recruiting participants through existing connections within the target population.
Data collection methods for qualitative nursing research vary depending on the chosen approach.
Common Data Collection Methods:
- Interviews: One-on-one conversations with participants, allowing for detailed exploration of their perspectives.
- Focus Groups: Facilitated discussions among a group of participants, exploring shared experiences and perspectives.
- Observations: Observing participants in their natural settings, documenting their behaviors and interactions.
- Document Analysis: Studying existing documents, such as medical records, patient journals, and organizational reports, to gain insights into the phenomenon of interest.
The data collected should be rich, detailed, and relevant to your research question.
4. Analyze and Interpret the Data
The analysis of qualitative data involves a process of identifying patterns, themes, and relationships within the collected data.
Methods for Qualitative Data Analysis:
- Thematic Analysis: Identifying key themes and patterns across the collected data.
- Content Analysis: Examining the content of text or other media to identify patterns and themes.
- Discourse Analysis: Analyzing the language and communication patterns within the data to understand how meaning is constructed and conveyed.
The goal of analysis is to develop a comprehensive and insightful understanding of the phenomenon under investigation, supported by rich textual evidence from your data.
Example:
- From interviews with nurses, you may identify recurring themes related to emotional exhaustion, such as lack of support, heavy workload, and difficulty balancing work and personal life.
5. Present Your Findings in a Qualitative Nursing Research Paper
Once your data is analyzed, you need to communicate your findings effectively in a well-structured and engaging qualitative nursing research paper.
Essential Components of a Qualitative Nursing Research Paper

- Introduction: Briefly introduce the topic, the research question, and the theoretical framework guiding your study.
- Literature Review: Provide an overview of existing research related to your topic, highlighting the knowledge gap your study addresses.
- Methodology: Describe the qualitative approach chosen, the sampling method, data collection methods, and data analysis techniques.
- Results: Present your findings in a clear and concise manner, using rich textual descriptions, direct quotes from participants, and tables or figures to illustrate key themes.
- Discussion: Interpret your findings in relation to existing literature and your theoretical framework. Discuss the significance of your findings for nursing practice, policy, and future research.
- Limitations: Acknowledge any limitations of your study, such as small sample size, potential biases, or specific methodological challenges.
- Conclusion: Summarize your findings and emphasize the key takeaways from your study.
- Recommendations: Provide practical recommendations for nursing practice, policy, or future research based on your findings.
6. Ensure Ethical Considerations
Ethical considerations are paramount in qualitative nursing research.
Key Ethical Principles:
- Informed Consent: Participants should be fully informed about the nature of the research, potential risks and benefits, and their right to withdraw at any time.
- Confidentiality and Anonymity: Participant data should be kept confidential and anonymous to protect their privacy.
- Beneficence: The research should aim to benefit participants or the wider nursing profession.
- Justice: Participants should be selected fairly and equitably, and the benefits and burdens of the research should be distributed fairly.
7. Disseminate Your Research
Sharing your research findings through publication or presentation is essential for advancing the field of nursing and informing best practices.
Opportunities for Dissemination:
- Peer-Reviewed Journals: Submit your qualitative nursing research paper to specialized nursing journals. That will enable you to reach a wider audience of academics and practitioners.
- Conferences: Present your research findings at professional nursing conferences to engage with colleagues and experts.
- Webinars and Online Platforms: Share your research findings through online platforms and webinars to reach a broader audience.
Qualitative Nursing Research Paper as a Tool for Change
Writing a compelling qualitative nursing research paper is a rigorous and rewarding process. By following the guidelines outlined above, you can craft a robust and impactful study that contributes to the body of knowledge and informs best practices in nursing. Remember, qualitative nursing research is a powerful tool for understanding the human experience, informing policy, and ultimately improving the quality of care provided to patients.
Through careful planning, ethical considerations, and a commitment to rigorous methodology, your qualitative nursing research paper can serve as a catalyst for positive change in nursing practice and beyond.
Get the Best Nursing Research Paper Writing Assistance
Writing a stellar qualitative nursing research paper can be one of the most daunting assignments. But, you can easily overcome the difficulties with professional nursing research paper writing help from Exemplary Dissertations. We have highly skilled writers to assist you in crafting original and engaging nursing essays, research papers, case studies and dissertations.