The nursing dissertation literature review is more than just a summary of existing research; it's the foundation upon which your own study will stand. It's a critical analysis of the current state of knowledge within your chosen field, showcasing your understanding of the topic, identifying gaps in the research, and ultimately justifying your dissertation's contribution. This process can seem daunting, but with the right approach, you can craft a comprehensive and impactful nursing dissertation literature review.
What is a Literature Review?
A literature review is a comprehensive and critical analysis of existing research on a specific topic. It's like a research paper that summarizes, evaluates, and synthesizes the findings of other studies.
Here's a breakdown of the key aspects of a nursing dissertation literature review:
Purpose:
- Inform: Provide an overview of what is known about a topic.
- Evaluate: Assess the strengths, weaknesses, and gaps in existing research.
- Synthesize: Combine different perspectives and theories to create a coherent understanding.
- Identify: Potential areas for future research.
Key Features:
- Focused topic: Reviews a specific research question or area of interest.
- Systematic approach: Follows a structured method for searching, selecting, and analyzing literature.
- Critical evaluation: Assesses the quality, relevance, and limitations of each source.
- Organized structure: Presents information in a logical and coherent manner, often using themes or categories.
- Clear argument: Offers a critical analysis and interpretation of the findings, drawing conclusions and highlighting key insights.
Benefits:
- Provides context: Helps understand your topic within the broader body of knowledge.
- Identifies research gaps: Helps you find areas where more research is needed.
- Avoids redundancy: Prevents you from repeating what is already known.
- Enhances credibility: Demonstrates your knowledge and understanding of the subject.
- Provides a foundation: Serves as the basis for your own research or project.
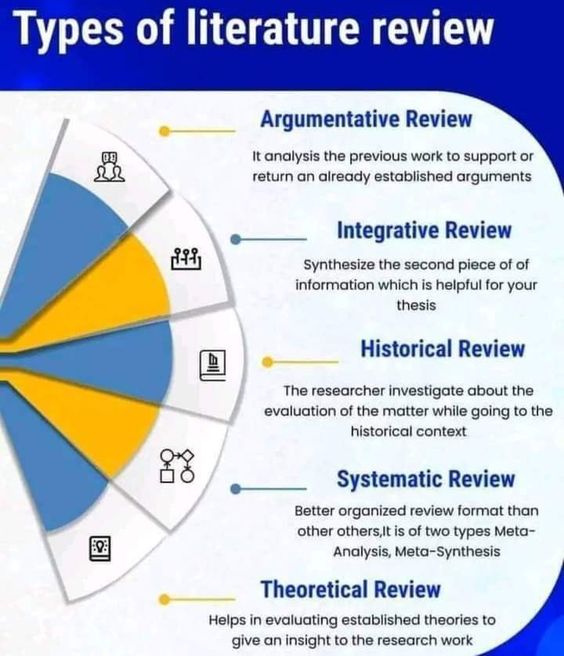
Types of Literature Reviews:
- Narrative: Tells a story about the topic, often chronological.
- Systematic: Follows a rigorous protocol for searching and selecting studies.
- Meta-analysis: Statistically combines findings from multiple studies.
- Thematic: Organizes the review around specific themes or concepts.
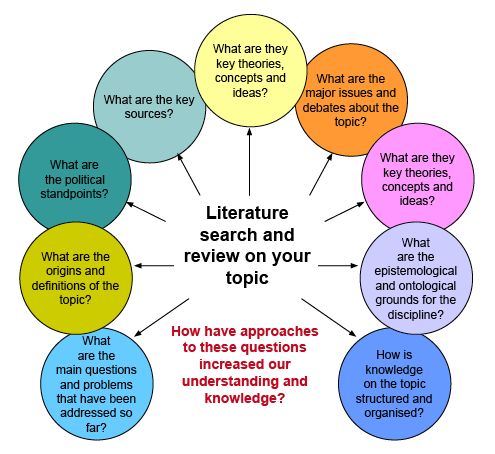
Overall, a literature review is an essential step in any research process. It helps you to become an expert on your topic, identify gaps in the literature, and develop your own research question or argument.
How to Write a Compelling Nursing Dissertation Literature Review
1. Define Your Research Question:
Before you dive into the ocean of research, you need a clear map. Your dissertation's research question will guide your entire journey, including the literature review. Ensure your question is specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). A well-defined question will help you focus your search and select relevant studies. For example, instead of broadly examining "patient satisfaction," you might ask, "How does implementing a standardized pain management protocol affect patient satisfaction in post-operative orthopedic surgery?"
2. Conduct a Rigorous Search:
Your nursing dissertation literature review relies on a thorough search for relevant studies. Start by identifying key terms related to your research question. Consider using a combination of keywords, subject headings, and Boolean operators (AND, OR, NOT) to refine your search. Explore databases specific to nursing research, such as CINAHL (Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature), PubMed, and PsycINFO. Don't forget to consult relevant professional journals and conference proceedings. Established academic platforms such as Nursing Papers can also provide a wealth of scholarly materials for research.
3. Critically Appraise the Literature:
Once you've gathered a collection of studies, it's time to critically assess their quality and relevance. Use appraisal tools specifically designed for research articles in your field. Assess the study's methodology, data collection, analysis, and conclusions. Look for potential biases, limitations, and inconsistencies. This critical appraisal will help you identify strengths and weaknesses within the existing literature.
4. Organize Your Findings:
A structured approach is key for a strong nursing dissertation literature review. Organize your findings into thematic categories related to your research question. This could include factors influencing patient outcomes, effectiveness of different interventions, or disparities in access to healthcare. Consider using a framework or model to further guide your organization.
5. Synthesize and Analyze the Literature:
Don't simply list findings from different studies. Your nursing dissertation literature review should synthesize and analyze the existing research. Identify common themes, trends, and discrepancies. Compare and contrast findings across different studies, paying attention to their methodological variations. This synthesis will help you develop a comprehensive understanding of the current state of knowledge and identify potential gaps in the literature.
6. Identify the Gaps in the Literature:
The nursing dissertation literature review is not only about summarizing existing research; it's also about identifying areas where knowledge is lacking. This is where your research question comes into play. By critically analyzing the literature, you can pinpoint gaps that your study can address. For instance, you might find that while several studies have investigated the effects of different pain management strategies, none have specifically focused on a standardized protocol in post-operative orthopedic surgery. This gap provides a strong justification for your dissertation.
7. Justify Your Research:
The nursing dissertation literature review is your opportunity to convince your reader that your research is necessary and valuable. Clearly articulate how your study will fill the identified gaps in the literature. Explain how your findings will contribute to existing knowledge, inform clinical practice, or shape future research in the field.
8. Maintain an Objective and Critical Tone:
While your nursing dissertation literature review should reflect your own understanding of the field, it's important to maintain an objective and critical tone. Avoid subjective opinions or personal biases. Focus on presenting the evidence from different studies and allow readers to draw their own conclusions.
9. Pay Attention to Formatting and Citations:
Follow the guidelines of your institution and the chosen journal (if applicable) for formatting and citations. Use consistent citation style throughout the literature review, ensuring accurate and complete references. Avoid plagiarism by paraphrasing and citing sources appropriately.
10. Engage with the Literature:
Your nursing dissertation literature review shouldn't be a dry recitation of facts. Engage with the literature by making connections between different studies, discussing potential implications of findings, and posing questions for further research. Use transition words and phrases to create a clear and logical flow.
11. Craft a Compelling Introduction and Conclusion:
The introduction to your nursing dissertation literature review should set the stage for your study. Provide context, define key terms, and introduce your research question. The conclusion should summarize the key findings and their implications. Highlight the gaps in the literature that your research will address and briefly describe your proposed study.
12. Refine and Revise:
Once you've completed the initial draft, take time to revise and refine your nursing dissertation literature review. Check for clarity, conciseness, and coherence. Ensure that the flow of ideas is logical and that the arguments are well-supported. Seek feedback from mentors, peers, or colleagues to improve the overall quality of your work.
Common Mistakes in Dissertation Literature Reviews and How to Avoid Them
Writing a literature review for your dissertation is crucial for demonstrating your understanding of the field and laying the foundation for your research. Here are some common mistakes and how to avoid them:
1. Lack of Focus:
- Mistake: Your review is too broad or lacks a clear argument or purpose.
- Avoid:
- Define your research question: Ensure your literature review directly relates to your research question and contributes to answering it.
- Develop a clear thesis statement: State your argument or perspective on the existing literature and how your research will contribute to it.
- Organize your review around themes and sub-themes: Group related studies and discuss them in a structured way.
2. Superficial Coverage:
- Mistake: You simply summarize studies without critically analyzing them or drawing connections.
- Avoid:
- Go beyond summarizing: Analyze the strengths and weaknesses of each study, identify gaps in knowledge, and highlight inconsistencies or controversies.
- Compare and contrast different perspectives: Show how different studies relate to each other and how your research fits into the bigger picture.
3. Ignoring Relevant Literature:
- Mistake: You miss important studies or overlook key literature in your field.
- Avoid:
- Conduct a thorough search: Utilize databases, journals, and other reliable sources to ensure you cover a wide range of relevant research.
- Consult experts: Seek advice from your advisor or other researchers in your field to ensure you're not missing crucial sources.
4. Inconsistent Structure and Style:
- Mistake: Your literature review lacks a consistent structure and style, making it difficult to follow.
- Avoid:
- Use clear headings and subheadings: Organize your review logically and use consistent formatting.
- Follow citation guidelines: Choose a specific citation style (APA, MLA, Chicago, etc.) and adhere to it throughout your review.
5. Lack of Critical Analysis:
- Mistake: You present the literature without offering your own insights or interpretations.
- Avoid:
- Synthesize the literature: Explain how the studies contribute to your understanding of the research problem.
- Present your own arguments: Draw connections, highlight key findings, and offer your perspective on the existing research.
6. Poor Writing:
- Mistake: You use jargon, passive voice, or overly complex language.
- Avoid:
- Write clearly and concisely: Use active voice and avoid unnecessary technical terms.
- Proofread and edit carefully: Ensure your writing is free of grammatical and spelling errors.
7. Ignoring Ethical Considerations:
- Mistake: You fail to acknowledge the limitations of the literature or potentially biased perspectives.
- Avoid:
- Acknowledge limitations: Be transparent about any shortcomings of the literature you reviewed.
- Consider diverse perspectives: Include studies from various researchers and represent different viewpoints to ensure a balanced and objective review.

Writing a nursing dissertation literature review is a challenging but rewarding process. It allows you to become an expert in your chosen field, identify critical gaps in the knowledge, and contribute to the advancement of nursing research. By following these strategies, you can craft a compelling and impactful nursing dissertation literature review that will serve as a strong foundation for your dissertation. Remember, your nursing dissertation literature review is a testament to your dedication to advancing the field of nursing. It's not just a requirement; it's an opportunity to make a meaningful contribution to the body of knowledge. So, embrace the journey, approach it with rigor and passion, and let your nursing dissertation literature review illuminate the path towards impactful research.
By avoiding these common mistakes, you can ensure your literature review is a strong foundation for your dissertation, showcasing your understanding of the field and paving the way for your original contribution to knowledge.
Get Help with Writing a Nursing Dissertation Literature Review
Are you looking for help with writing a nursing dissertation literature review? Look no further than Exemplary Dissertations. We offer professional nursing dissertation writing help, covering all the sections of the assignments. We also do proof reading and editing, and plagiarism check and removal to ensure an original and compelling nursing dissertations, research papers, essays and case studies.