Nursing, at its core, is about caring for the whole person. It's about understanding not just the physical ailment, but also the emotional, social, and psychological factors that influence an individual's health and well-being. This holistic approach is brilliantly captured in Abraham Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs, a powerful framework that can enrich your nursing case study writing.
Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs: A Framework for Understanding the Human Condition
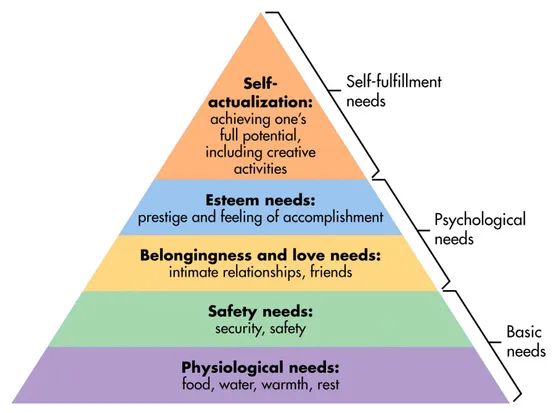
Maslow's theory proposes that human needs are arranged in a hierarchical order, with the most basic needs at the bottom and the most advanced at the top. This hierarchy serves as a guide for understanding human motivation and behavior, offering invaluable insights for nursing practice.
- Physiological Needs: These are the most fundamental, including basic survival needs like breathing, food, water, sleep, and homeostasis. When these needs are not met, individuals are unable to focus on anything else.
- Safety and Security Needs: Once physiological needs are met, individuals seek safety and security in their environment, including personal security, financial security, health and well-being, and stability.
- Love and Belonging Needs: These are the needs for social connection, love, belonging, acceptance, and intimacy.
- Esteem Needs: These needs involve self-esteem, confidence, achievement, respect from others, and recognition.
- Self-Actualization Needs: This is the highest level of Maslow's hierarchy and involves fulfilling one's potential, achieving personal growth, and living a meaningful life.
Integrating Maslow's Hierarchy into Your Nursing Case Study
By incorporating Maslow's Hierarchy into your nursing case study, you can elevate your analysis and showcase your understanding of the patient's holistic needs. Here's a step-by-step guide to guide you through the process:
Step 1: Selecting a Nursing Case Study
Choose a nursing case study that allows you to delve into the patient's journey, encompassing their physical, emotional, and social aspects. A diverse range of case studies can be used, from chronic illness management to acute care scenarios, allowing you to apply the framework to varying patient needs.
Step 2: Gathering Patient Data
Gather comprehensive data about your patient. This includes:
- Medical History: Review the patient's medical history, including previous illnesses, surgeries, medications, and allergies.
- Current Health Status: Document the patient's presenting symptoms, vital signs, and current medical diagnosis.
- Social History: Gather information about the patient's family structure, living situation, occupation, cultural background, and support system.
- Psychosocial Assessment: Evaluate the patient's mental health, emotional well-being, coping mechanisms, and any contributing psychosocial factors.
Step 3: Analyzing the Case Study Through Maslow's Hierarchy
Analyze the collected data through the lens of Maslow's Hierarchy. Ask yourself:
- Which needs are being met? Identify the needs that are currently being addressed for your patient.
- Which needs are unmet? Determine which needs are not being met and are potentially contributing to the patient's current health challenges.
- How do these unmet needs impact the patient's overall well-being? Explore the direct and indirect consequences of unmet needs on the patient's physical, emotional, and social health.
- What are the underlying factors contributing to the unmet needs? Uncover the root causes of unmet needs, such as personal circumstances, social determinants of health, or systemic barriers.
Step 4: Developing Nursing Interventions
Based on your analysis, identify nursing interventions that address the unmet needs of your patient. The nurse should individualize and tailor those interventions to the specific needs and circumstances of the patient.
- Physiological Needs: Prioritize interventions that ensure the patient's basic survival needs are met, such as pain management, hydration, nutrition, and adequate rest.
- Safety and Security Needs: Address any concerns regarding the patient's safety and security, providing a safe environment, offering reassurance, and empowering them with information.
- Love and Belonging Needs: Facilitate social connection, encourage support from family and friends, and provide emotional support to address the patient's need for connection and belonging.
- Esteem Needs: Boost the patient's self-esteem by acknowledging their strengths, providing positive reinforcement, and encouraging their participation in decision-making.
- Self-Actualization Needs: Support the patient's personal growth and development by providing opportunities for self-expression, creativity, and meaningful activities.
Step 5: Evaluating Outcomes and Refining Interventions
Continuously evaluate the effectiveness of your nursing interventions and adapt them as needed.
- Monitor the patient's progress: Assess the patient's physical, emotional, and social well-being to determine if interventions are addressing the unmet needs.
- Identify any barriers: Analyze any obstacles that hinder the effectiveness of your interventions and brainstorm solutions to overcome these barriers.
- Adjust interventions: Modify interventions based on the patient's response and progress.
Examples of Nursing Case Studies Utilizing Maslow's Hierarchy
Case Study 1: A Patient with Chronic Pain
Ms. Jones is a 65-year-old woman, admitted to the hospital with chronic back pain. She has been experiencing pain for several years, which limits her mobility and participation in daily activities.
- Analysis: Ms. Jones's unmet needs include physiological needs (pain management) and safety and security needs (fear of further injury).
- Interventions: The nurse implements interventions focused on pain relief through medication, physical therapy, and alternative therapies. The nurse also educates Ms. Jones on safety precautions to minimize further pain and promotes a sense of security by providing emotional support and reassurance.
Case Study 2: A Patient with Depression
Mr. Smith is a 28-year-old man, admitted to the psychiatric unit with major depressive disorder. He reports feeling hopeless, isolated, and unable to participate in his usual activities.
- Analysis: Mr. Smith's unmet needs include love and belonging needs (feelings of isolation and loneliness) and esteem needs (low self-worth and lack of confidence).
- Interventions: The nurse prioritizes interventions focused on fostering social connection, providing therapeutic support groups, and promoting positive self-talk. The nurse also encourages Mr. Smith to engage in activities that boost his confidence and provide a sense of accomplishment.
Case Study 3: A Patient with a Terminal Illness
Ms. Brown is a 72-year-old woman, diagnosed with terminal cancer. She is struggling to cope with her diagnosis and the impending loss of her independence.
- Analysis: Mrs. Brown's unmet needs include safety and security needs (fear of the unknown and loss of control), love and belonging needs (desire for support and connection), and self-actualization needs (seeking meaning and purpose in her final days).
- Interventions: The nurse focuses on providing compassionate support, facilitating open communication with family members, and offering spiritual guidance. The nurse also encourages Mrs. Brown to engage in meaningful activities that bring her joy and peace.
Benefits of Using Maslow's Hierarchy in Nursing Case Studies
Incorporating Maslow's Hierarchy into your nursing case study offers numerous benefits:
- Enhanced understanding of the patient's experience: This framework allows you to grasp the full scope of the patient's needs and how they contribute to their overall well-being.
- Development of holistic nursing interventions: You can create interventions that address the patient's physical, emotional, and social needs, promoting their holistic health.
- Improved patient care: By focusing on the patient's unmet needs, you can provide personalized and effective care that improves their quality of life.
- Strengthened nursing skills: Utilizing Maslow's Hierarchy fosters critical thinking, problem-solving, and communication skills, making you a more skilled and empathetic nurse.
Ethical Considerations
When working with patients, it's crucial to consider ethical implications. Respect for patient autonomy, confidentiality, and cultural sensitivity are paramount. Remember to obtain informed consent for any interventions and tailor your approach to the patient's individual values and beliefs.

Common Mistakes to Avoid in Nursing Case Studies
Writing a compelling and insightful nursing case study requires not only a strong understanding of the patient's situation but also a mastery of the writing craft. While the framework of Maslow's Hierarchy can be incredibly helpful, neglecting crucial writing elements can detract from the impact of your work. Here's a breakdown of common mistakes and how to avoid them:
1. Lack of Clear Focus and Purpose:
- Mistake: The case study lacks a clear thesis statement or research question, leaving the reader confused about the purpose and direction of the study.
- Solution: Develop a strong thesis statement that outlines the key focus of the case study and the main message you want to convey. This acts as a roadmap for both you and your reader. For example, "This case study examines how a patient with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) experienced an exacerbation of symptoms due to unmet safety and security needs related to their home environment."
2. Insufficient Patient Data and Analysis:
- Mistake: The case study relies on superficial information, failing to adequately present the patient's background, health history, and current situation. This leads to a shallow and unconvincing analysis.
- Solution: Gather comprehensive patient data, including medical history, social history, psychosocial assessment, and current medical records. This forms the foundation for a thorough analysis, revealing the patient's complex needs and experiences.
3. Overreliance on Medical Terminology:
- Mistake: The study overwhelms the reader with technical jargon, making it inaccessible and difficult to understand.
- Solution: Use clear, concise language, and explain any complex medical terms in accessible terms. Aim for a balance between medical accuracy and comprehensibility. If necessary, use a glossary of terms to help readers understand specific concepts.
4. Insufficient Application of Theoretical Framework:
- Mistake: The case study mentions the framework (like Maslow's Hierarchy) but fails to demonstrate how it informs the analysis and guides the development of interventions.
- Solution: Explicitly tie the analysis and interventions to the chosen framework. Explain how the patient's needs align with specific levels of the hierarchy and how understanding these needs influences your actions.
5. Neglecting the Patient's Perspective:
- Mistake: The case study focuses solely on the medical aspects, neglecting the patient's subjective experiences, feelings, and values.
- Solution: Include direct quotes from the patient, their family, or caretakers to bring the story to life. Emphasize the patient's own interpretation of their illness, their coping mechanisms, and their hopes for the future.
6. Weakly Presented Interventions:
- Mistake: The interventions are not clearly defined, lack rationale, or fail to demonstrate their connection to the identified needs.
- Solution: Outline each intervention with clear steps and justifications. Explain how these interventions directly address the unmet needs identified through the Maslow's Hierarchy analysis. Be specific about the techniques, tools, and resources used.
7. Lack of Outcome Evaluation:
- Mistake: The case study concludes without a clear assessment of the interventions' effectiveness and the patient's progress.
- Solution: Describe how the patient's health and well-being were impacted by the interventions. Include objective data (e.g., vital signs, lab results) and subjective feedback from the patient and family. Explain any challenges faced and how these were addressed.
8. Poor Writing Style and Organization:
- Mistake: The case study is poorly formatted, contains grammatical errors, and lacks a logical flow.
- Solution: Use a clear and concise writing style. Follow established guidelines for formatting and citations. Ensure proper grammar, spelling, and punctuation. Organize your writing into logical sections with clear headings and subheadings.
9. Ignoring Ethical Considerations:
- Mistake: The case study fails to address ethical implications of the interventions or patient care.
- Solution: Address any ethical dilemmas encountered and explain how you, as a nurse, navigated these situations. Discuss the principles of patient autonomy, beneficence, non-maleficence, and justice in relation to the case study.
10. Limited Impact and Generalizability:
- Mistake: The case study fails to draw meaningful conclusions or offer practical insights for other nursing professionals.
- Solution: Conclude with a discussion of the case study's implications for future nursing practice. Identify key learning points, suggest potential applications of the findings to similar situations, and recommend further research.
By diligently addressing these common mistakes, you can elevate your nursing case study writing to a new level of sophistication and impact. Remember, the aim is to create a compelling and insightful narrative that not only presents a patient's story but also contributes to the understanding and improvement of nursing practice.
Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs provides a powerful lens for understanding the human experience, particularly in the context of nursing. By integrating this framework into your nursing case study, you can enhance your analysis, develop effective interventions, and ultimately provide compassionate and holistic care to your patients. Remember, every patient is unique, and their needs, whether they are physiological, safety, love, esteem, or self-actualization, are integral to their well-being. As you delve into the nursing case study, let Maslow's Hierarchy guide you, empowering you to write a story that not only reflects the patient's physical ailments but also celebrates their humanity.
Get Customized Nursing Case Study Writing Help
Are you looking for help in writing a nursing case study using Maslow’s hierarchy of needs? Then, look no further than Exemplary Dissertations for custom nursing case study writing assistance. We specialize in professional writing services for nursing case studies, research papers, essays and dissertations. Our service covers topic suggestion, paper writing, proof reading, editing, and plagiarism removal.