Embarking on a dissertation is a significant undertaking, often representing the culmination of years of study. The foundation of a successful dissertation lies in selecting the right topic. A well-chosen topic will not only sustain your interest throughout the research process but also allow you to make a meaningful contribution to your field. However, choosing a dissertation topic can feel daunting, especially with the vast array of potential avenues to explore.
This comprehensive guide aims to provide a roadmap for navigating the complexities of choosing a dissertation topic, ensuring that you embark on your research journey with confidence and clarity. We'll explore key considerations, practical strategies, and essential resources to help you identify a research area that is both intellectually stimulating and academically viable.
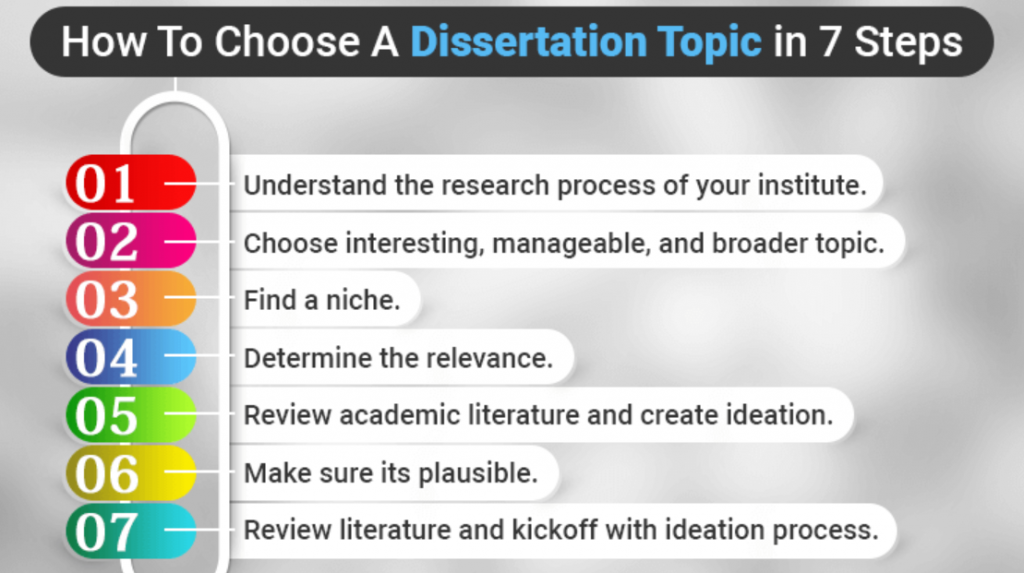
I. Laying the Groundwork: Understanding the Fundamentals
Before diving into specific topic ideas, it's crucial to establish a solid foundation by understanding the core principles that underpin successful dissertation research.
1. Defining Your Research Interests:
- Reflect on Your Past Coursework: What subjects resonated with you most? Were there any particular lectures, readings, or assignments that sparked your intellectual curiosity?
- Consider Your Personal Passions: A dissertation is a long-term commitment. Selecting a topic that genuinely interests you will make the process more enjoyable and less of a chore.
- Identify Emerging Trends in Your Field: What are the current debates and hot topics within your discipline? Exploring emerging trends can lead to innovative and impactful research.
2. Understanding Your Program Requirements:
- Review the Dissertation Guidelines: Your university's dissertation guidelines will outline specific requirements regarding the scope, methodology, and length of your dissertation.
- Consult with Your Supervisor: Your supervisor can provide invaluable guidance on the suitability of your potential topics and offer insights into the faculty's research interests.
- Familiarize Yourself with Ethical Considerations: Research involving human subjects or sensitive data requires careful consideration of ethical implications.
3. Assessing Your Resources and Skills:
- Evaluate Your Research Skills: Are you proficient in quantitative or qualitative research methods? Do you have access to relevant data sources?
- Consider Your Time Constraints: Dissertation research requires a significant time investment. Choose a topic that can be realistically completed within the allotted timeframe.
- Assess Your Access to Resources: Do you have access to libraries, databases, and other resources necessary to conduct your research?
II. Brainstorming and Refining Potential Topics
Once you have a solid understanding of the fundamentals, it's time to brainstorm potential dissertation topics. This process should be creative and exploratory, allowing you to generate a wide range of ideas.
1. Techniques for Generating Ideas:
- Literature Review: Conduct a thorough review of existing literature in your field. Identify gaps in knowledge, conflicting findings, or areas that warrant further investigation.
- Mind Mapping: Use mind mapping techniques to visually represent your research interests and explore potential connections between different concepts.
- Discussions with Experts: Engage in conversations with professors, researchers, and practitioners in your field. Their insights can provide valuable perspectives and generate new ideas.
- Attending Conferences and Seminars: Attending academic conferences and seminars can expose you to cutting-edge research and inspire new research directions.
2. Refining Your Ideas:
- Specificity is Key: Vague or overly broad topics are difficult to manage. Narrow down your focus to a specific research question or problem.
- Assess Feasibility: Is your research question answerable within the scope of a dissertation? Do you have access to the data or resources required to conduct your research?
- Ensure Significance: Will your research make a meaningful contribution to your field? Will it address a significant problem or advance our understanding of a particular phenomenon?
- Consider Novelty: While originality is not always essential, exploring a novel angle or perspective can enhance the impact of your research.
3. Practical Strategies for Narrowing Down Your Choices:
- Develop a Preliminary Research Proposal: Outline your research question, methodology, and anticipated findings. This will help you assess the feasibility and scope of your project.
- Conduct a Pilot Study: A small-scale pilot study can help you test your research methods and identify potential challenges.
- Seek Feedback from Others: Share your ideas with your supervisor, peers, and other experts in your field. Their feedback can help you refine your research question and improve your methodology.

III. Evaluating and Finalizing Your Dissertation Topic
After generating a list of potential topics, it's time to evaluate their suitability and finalize your choice. This involves a critical assessment of the feasibility, significance, and originality of each topic.
1. The "So What?" Test:
- Significance: Does your research address a significant problem or contribute to a broader understanding of a particular phenomenon?
- Impact: Will your research have practical implications for policy or practice? Will it inform future research in your field?
- Audience: Who will be interested in your research findings? Will your research be relevant to academics, practitioners, or the general public?
2. Feasibility Assessment:
- Time Constraints: Can you realistically complete the research within the allotted timeframe?
- Resource Availability: Do you have access to the data, resources, and expertise required to conduct your research?
- Ethical Considerations: Are there any ethical challenges associated with your research? Can these challenges be addressed effectively?
3. Originality and Contribution:
- Novelty: Does your research offer a new perspective or approach to a particular problem?
- Contribution: Will your research add to the existing body of knowledge in your field? Will it challenge existing assumptions or theories?
- Uniqueness: Is your research sufficiently different from other studies in your field?
4. Refining your Research Question:
- Clarity: Is your research question clear, concise, and unambiguous?
- Focus: Is your research question focused enough to be manageable within the scope of a dissertation?
- Answerability: Is your research question answerable using available data and research methods?
5. Seeking Final Approval from Your Supervisor:
- Present your chosen topic and refined research question to your supervisor.
- Be prepared to discuss the rationale for your topic choice, the feasibility of your research plan, and the potential contribution of your work.
- Incorporate your supervisor's feedback into your final dissertation proposal.
Choosing a dissertation topic is a crucial step that demands careful consideration and strategic planning. Don't rush the process. Take your time to explore your interests, assess your resources, and refine your research question.
IV. Resources and Support for Dissertation Topic Selection
Navigating the dissertation process can be challenging, and seeking help with choosing a dissertation topic can be immensely beneficial. Universities and other organizations offer a range of resources to support students in their research endeavors.
1. University Resources:
- Supervisors: Your supervisor is your primary source of support and guidance. They can provide feedback on your topic ideas, help you refine your research question, and offer advice on methodology.
- Library Resources: University libraries offer access to a vast collection of books, journals, and databases. Librarians can assist you with literature searches and provide training on research methods.
- Writing Centers: Writing centers offer support with all aspects of the writing process, including dissertation proposal development, literature review, and manuscript editing.
- Research Centers: Many universities have research centers that focus on specific areas of study. These centers can provide access to data, equipment, and expertise.
2. Online Resources:
- Academic Databases: Databases such as JSTOR, Scopus, and Web of Science provide access to scholarly articles and research papers.
- Online Forums and Communities: Online forums and communities can provide a supportive environment for students working on their dissertations.
- Dissertation Examples: Reviewing completed dissertations in your field can provide valuable insights into topic selection, methodology, and writing style.
3. Consulting with Experts:
- Professors and Researchers: Reach out to professors and researchers in your field to discuss your research interests and seek their advice on topic selection.
- Practitioners: If your research has practical implications, consider consulting with practitioners in the field to gain insights into real-world challenges and opportunities.
How to choose a dissertation topic is a skill that develops with practice and guidance. Don't hesitate to seek support from your university, online resources, and experts in your field.
V. Common Pitfalls to Avoid when Choosing a Dissertation Topic
While choosing a topic for dissertation the process can be exciting, there are common pitfalls to avoid that can derail your research efforts.
- Choosing a Topic That is Too Broad: A broad topic will be difficult to manage and will likely result in a superficial analysis.
- Choosing a Topic That is Too Narrow: A narrow topic may not have enough scope for a dissertation-length project.
- Choosing a Topic That is Over-Researched: If a topic has been extensively researched, it may be difficult to make a significant contribution.
- Choosing a Topic That Does Not Align with Your Interests: If you are not genuinely interested in your topic, you will likely struggle to stay motivated throughout the research process.
- Ignoring Program Requirements: Failing to adhere to your program's dissertation guidelines can lead to delays and complications.
The Power of Perseverance
Choosing a dissertation topic is not a linear process. It may involve several iterations of brainstorming, refining, and evaluating. Don't be discouraged if you encounter setbacks or challenges along the way.
- Stay Persistent: Keep exploring your interests and seeking feedback from others.
- Be Flexible: Be willing to adapt your topic or research question as you learn more about your field.
- Maintain a Positive Attitude: Believe in your ability to complete your dissertation successfully.
Concluding Remarks on Choosing a Dissertation Topic
Ultimately, the best dissertation topics are those that are both intellectually stimulating and academically viable. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can increase your chances of choosing a dissertation topic that is a perfect fit for your skills, interests, and career goals. Remember that choosing a dissertation topic is a journey, not a destination. Embrace the challenges, celebrate the successes, and enjoy the process of discovery.
At Exemplary Dissertations, we help students with topic suggestion, dissertation writing, proofreading, editing, formatting and plagiarism removal. We guarantee a compelling topic and high quality paper that will truly set you up for academic success. Our experienced writers can also assist you with crafting research papers, essays and case studies.