The PhD dissertation, a culmination of years of dedicated research and intellectual inquiry, is a monumental undertaking. It represents the pinnacle of a doctoral candidate’s academic journey, showcasing their original contribution to their field and marking their transition from student to scholar. However, the task of crafting a successful PhD dissertation can be daunting.
With a vast amount of information to synthesize, meticulous analysis to perform, and a compelling narrative to weave, it is crucial to understand the essential components that make up this complex document.
The Key Elements of a Stellar PhD Dissertation
1. The Introduction: Setting the Stage for Your Research
The introduction is the cornerstone of your PhD dissertation, laying the foundation for the entire argument you will present. It is the first impression you make on your readers, and it must capture their attention and pique their curiosity. A well-crafted introduction should:
- Define the research problem: Clearly articulate the specific gap in knowledge that your PhD dissertation seeks to address. This should be a problem that is both significant and relevant to your field.
- Establish the research questions: These are the guiding inquiries that drive your research and will be answered throughout the dissertation. They should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
- Provide an overview of the research methodology: Briefly outline the theoretical framework, research design, and data collection methods you will employ. This informs the reader of the approach you will take to answer your research questions.
- Present the significance of your research: Highlight the practical and theoretical implications of your findings, demonstrating the value of your contribution to the field.
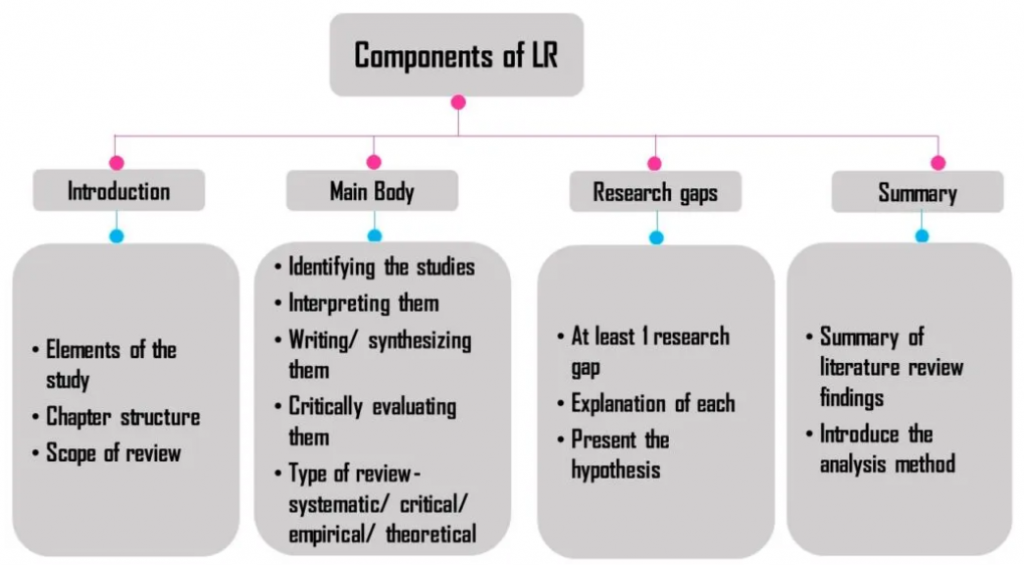
2. The Literature Review: Building a Foundation of Knowledge
The literature review is a critical component of any PhD dissertation. It serves as a comprehensive survey of existing scholarship on your chosen topic, demonstrating your mastery of the relevant literature and situating your own research within the broader context of the field. A strong literature review should:
- Identify key concepts and theories: Define and explain the major concepts and theoretical frameworks that are relevant to your research.
- Analyze and synthesize existing research: Go beyond simply summarizing the literature. Critically analyze and synthesize the findings of previous studies, identifying key themes, trends, and debates.
- Highlight the gaps in existing research: This is where you identify the specific area of knowledge that your PhD dissertation will address. It demonstrates the need for your own research and its potential contribution to the field.
- Establish the foundation for your own research: The literature review should smoothly transition into the methodology and results sections of your PhD dissertation, providing a clear context for your own research and analysis.
3. The Methodology: The Heart of Your Research
The methodology section of your PhD dissertation outlines the specific methods you used to collect and analyze data, ensuring that your research is replicable and credible. A strong methodology section should:
- Provide a detailed description of your research design: This includes the type of study you conducted (e.g., quantitative, qualitative, mixed methods), the specific research methods used (e.g., surveys, interviews, experiments), and any ethical considerations that were addressed.
- Justify your choice of methodology: Explain why your chosen methods are appropriate for addressing your research questions and the limitations of your chosen approach.
- Explain the data collection procedures: Provide detailed information on how you collected your data, including the sampling strategy, data sources, and any instruments used.
- Describe the data analysis techniques: Clearly explain how you analyzed your data, including the software or statistical methods used.
4. The Results: Presenting Your Findings
The results section of your PhD dissertation presents the findings of your research, providing a clear and concise summary of your data and analysis. This section should be:
- Factual and objective: Present your findings without interpretation or commentary. Stick to the facts and avoid drawing conclusions.
- Organized and structured: Present your findings in a clear and logical order, using tables, figures, and charts to illustrate your data.
- Supported by evidence: Every claim made in the results section should be supported by data from your research.
5. The Discussion: Interpreting and Analyzing Your Findings
The discussion section of your PhD dissertation provides an interpretation of your findings, linking them back to your research questions and the broader field of study. This section should:
- Summarize your findings: Provide a concise overview of the most significant findings of your research.
- Interpret the meaning of your findings: Discuss the implications of your findings for your research questions, and explain what they mean in the context of your chosen field.
- Relate your findings to previous research: Compare your findings to the literature review, highlighting areas of agreement and disagreement, and discussing the contributions your research makes to the field.
- Identify limitations of your study: Acknowledge any shortcomings or limitations of your research, providing a balanced assessment of its strengths and weaknesses.
6. The Conclusion: A Synthesis of Your Research
The conclusion of your PhD dissertation is your final opportunity to summarize your research, highlight its key contributions, and suggest future directions for research. A strong conclusion should:
- Restate your research questions and answer them: Clearly summarize the research questions that guided your work and provide a concise answer to each one.
- Reiterate the significance of your findings: Highlight the importance of your findings and discuss their potential implications for future research, policy, and practice.
- Suggest areas for future research: Identify areas where your research could be expanded upon or taken in new directions, providing a roadmap for further exploration of your chosen field.
7. The Appendices: Supporting Your Research
The appendices of your PhD dissertation contain supplemental materials that provide further information and context for your research. These may include:
- Raw data: Data tables, questionnaires, interview transcripts, or other primary data sources.
- Statistical analysis: Detailed statistical analyses, including output from software programs.
- Research instruments: Surveys, interview guides, or other tools used to collect data.
- Other supporting documents: Letters of permission, IRB approvals, or other relevant documents.

The Art of Writing a PhD Dissertation: Beyond the Components
While understanding the essential components of a PhD dissertation is crucial, it is only the first step in the journey. The true art of writing a successful PhD dissertation lies in the ability to weave these components together into a cohesive and compelling narrative. This involves:
- Developing a strong argument: Craft a clear and logical argument that supports your research questions and justifies your findings.
- Using clear and concise language: Write in a scholarly tone, using precise and specific language that is accessible to your readers.
- Structuring your dissertation effectively: Organize your dissertation into clear and logical sections, using headings, subheadings, and transitions to guide the reader through your argument.
- Engaging with the literature: Integrate relevant scholarship throughout your dissertation, demonstrating your mastery of the field and providing a context for your own research.
- Citing your sources meticulously: Follow the appropriate citation style guidelines to ensure the accuracy and credibility of your work.
The PhD Dissertation: A Gateway to Scholarly Success
The PhD dissertation is a demanding but rewarding undertaking. It is an opportunity to make a meaningful contribution to your field and to develop your skills as a researcher and scholar. By understanding the essential components of this complex document and mastering the art of writing a compelling narrative, you can embark on this journey with confidence and emerge as a capable and accomplished scholar.
Frequently Asked Questions about PhD Dissertation Writing
1. What is the Purpose of a PhD Dissertation?
The PhD dissertation is the culmination of your doctoral studies. It’s a substantial piece of original research that demonstrates your ability to contribute to your field. It’s not just a longer version of a master’s thesis; it’s a unique, in-depth exploration of a specific research question.
2. How Long Does it Take to Write a PhD Dissertation?
There’s no set timeframe, as it depends on factors like your research topic, methodology, and writing style. However, it typically takes several years of dedicated work to complete a PhD dissertation.
3. What Are the Different Sections of a PhD Dissertation?
The standard structure includes:
- Introduction: Contextualizes your research question and its significance.
- Literature Review: Summarizes existing research and identifies gaps you’ll address.
- Methodology: Explains your research approach, data collection, and analysis methods.
- Results: Presents your findings in a clear and organized manner.
- Discussion: Interprets your findings, links them to existing literature, and discusses limitations.
- Conclusion: Summarizes key findings and their implications.
- References: Lists all sources cited in your PhD dissertation.
4. How Do I Choose a Topic for My PhD Dissertation?
Choose a topic that interests you deeply and aligns with your research interests and expertise. It should be specific enough to be manageable yet broad enough to contribute to your field.
5. How Can I Avoid Procrastination While Writing My Dissertation?
Break down the task into smaller, manageable chunks and set realistic deadlines. Establish a consistent writing routine and seek support from your advisor and peers. Remember, writing a PhD dissertation is a marathon, not a sprint.
6. What Are the Most Common Mistakes to Avoid When Writing a PhD Dissertation?
- Lack of focus: Ensure your research question and argument are clear and concise.
- Poor organization: Structure your dissertation logically and use clear headings and subheadings.
- Insufficient evidence: Support your claims with strong evidence from reliable sources.
- Unclear writing: Use precise language and avoid jargon.
7. Where Can I Find Help with Writing My PhD Dissertation?
Seek guidance from your advisor, attend writing workshops, and utilize university resources such as the writing center. Don’t be afraid to ask for help; everyone struggles with dissertation writing at some point.
8. What Happens After I Finish Writing My PhD Dissertation?
You’ll need to defend your PhD dissertation in front of a committee of experts. They’ll evaluate your research and assess your ability to defend your findings. After successful defense, you’ll earn your PhD.

The PhD dissertation is not just a document; it is a testament to your intellectual growth, your dedication to your field, and your potential to make a lasting impact on the world of scholarship.
Get Professional Nursing Dissertation Help
At Exemplary Dissertations, we can help with all your dissertation projects, from research to writing. We provide an all-inclusive service that covers topic suggestion, dissertation writing, proofreading, formatting and plagiarism removal. We also offer customized assistance with research papers, essays and thesis.

